AmbienteDiritto.it - Rivista giuridica - Electronic Law Review - Tutti i diritti sono riservati - Copyright © - AmbienteDiritto.it
Testata registrata presso il Tribunale di Patti Reg. n. 197 del 19/07/2006
Food crops vs. Fuel crops: perspectives and policy options
PIETRO LANZINI*
Abstract
The paper
investigates if and to what extent a shift towards “fuel crops” production would
have beneficial impacts on the environment, focusing on the “competition for
land” issue. The question is whether an increase of biodiesel and bioethanol
production would hinder the “food crops” production, as a consequence of land
scarcity, with detrimental backlashes such as deforestation, harshening of
undernourishment emergency in developing countries, and so on.
Given the absence of an universally accepted answer to such a broad question,
the paper proposes the points of view and scientific instances of both
“doomsayers” and optimists, highlighting common ground where possible, such as
in the call for an increase of productivity of crops (to be achieved by
traditional or innovative methods).
After an analysis of the specific Brazilian case, where both benefits and
backlashes of the booming biofuel industry are investigated, the report ends
with an overview of current policy options that are being implemented in
developed as well as developing countries, and with a hint to an issue that is
beginning to gain great public attention: perspectives on biofuel certification.
Keywords:
biofuel, competition for land, Jatropha.
Introduction: biofuels trends and drivers
To date, fuels from crude oil supply most of the worldwide demand for primary
energy. Such dependence is clearly not ideal; not only because crude oil
reserves are limited and unevenly distributed in the world, with the most
important reserves in politically unstable regions, but also because of
environmental issues. On the wave of such concerns, there is a momentum for
throughout discussing the pros and cons of alternative energy sources, and the
present paper specifically focuses on one of them: biofuels. Biofuels are a
renewable energy that encompass a broad range of products, varying significantly
in terms of characteristics and environmental impacts. The following table
illustrates a list of biofuels, as in the EC Directive 2003/30:
|
bioethanol |
bio-ETBE |
|
biodiesel |
bio-MTBE |
|
biogas |
synthetic biofuels |
|
biomethanol |
biohydrogen |
|
biodimethylether |
pure vegetable oil |
We will especially focus our attention on liquid fuels from biomass, namely
bioethanol and biodiesel, being respectively ethanol produced from biomass
and/or the biodegradable fraction of waste, and a methyl-ester produced from
vegetable or animal oil (such as soybeans and oil seeds).
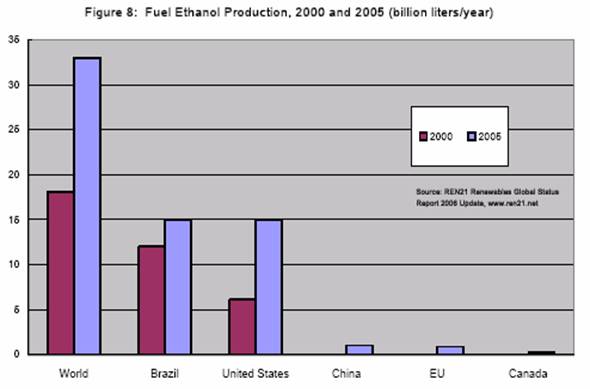
Biofuels production of 33 billion litres in 2004 is still small compared to
1,200 billion litres of gasoline produced annually worldwide, but it is on the
rise. Brazil has been the world’s leader (and primary user) of fuel ethanol for
more than 25 years, producing slightly less than half the world’s total in 2004.
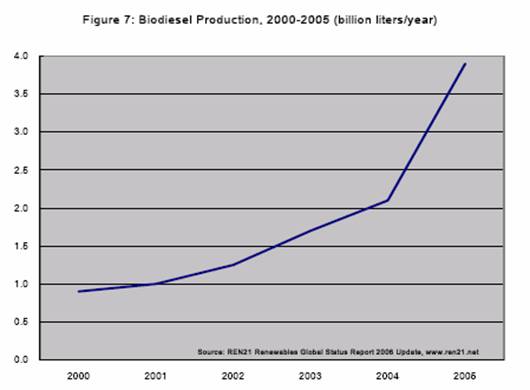
Total world production of bio-diesel in 2004 was more than 2 billion litres, of
which more than 90% was produced in the EU25 (Eurobserver 2005). The size and
continuous growth of biodiesel and fuel ethanol productions are well represented
by the following figures:

The increasing trend is not typical of recent years only, as we note taking a
look at the biofuel production over the past 30 years (Worldwatch institute
2006)1:
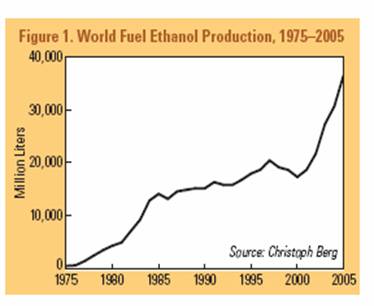
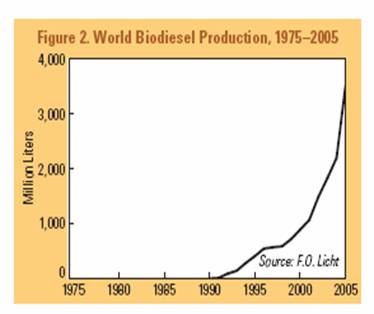
As far as biofuel producing countries are concerned, Brazil and the United
States play a crucial role in the bioethanol industry, while biodiesel industry
is greatly developed in Europe, as previously anticipated, and especially in
Germany (Worldwatch Institute 2006):
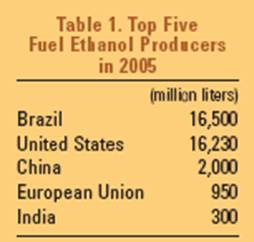
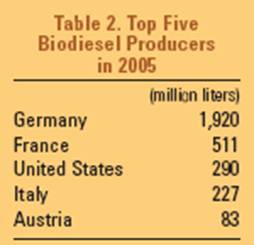
There are many drivers supporting such international development of biodiesel
production. While the list is not exhaustive, we summarize some of those drivers
below:
o The adoption of national-level targets in a number of countries for blending biofuels with petroleum fuels in response to concerns about energy security and GHG emissions. Both ethanol and biodiesel can be easily incorporated into blends and they can be used in existing motor fuel distribution networks without having to modify vehicles to any great extent.
o The potential for achieving reduction in GHG emissions and improving vehicle performance is regarded as a significant factor influencing biofuel use particularly in industrialized countries with reduction commitments under the Kyoto protocol.
o Enhancing rural economy in terms of added agro products and new markets as well as employment generation particularly in developing countries.
o New opportunities for trade with possibilities of exports from developing countries which are expected to produce biofuels at a relatively cheaper cost because of their lower labor costs.
o Soil protection and land reclamation can be enhanced, as growth of biomass feedstock can help restore degraded land, such as agricultural lands withdrawn from food production
o Great potential of turning a problem into a resource, as far as waste management is concerned: as millions of tons of waste and residues are produced every year, such stock of materials ranging from municipal solid wastes to animal wastes, from straw to rice husk and so on can be used to produce energy.
Biofuel production: feedstock and pathways
Biofuel can be produced from a wide range of crops and materials, as feedstock
varies significantly worldwide in relation to the climatic and geographical
features of a given region and to the technological and economic background of
such areas.
Biodiesel can be produced, for instance, from rapeseed, soybeans, sunflowers and
coconuts, while bioethanol comes from grains or seeds (like corn, wheat or
potato), sugar crops (sugar beets and sugarcane) or even from lignocellulose
biomass. Corn and soybeans are primarily grown in the United States, while
rapeseed is grown primarily in Europe, sugar cane in Brazil and palm oil in
South-East Asia. Moreover, biodegradable outputs from industry, agriculture,
forestry and households can be used to produce bioenergy, as well (e.g.: straw,
timber, sewage, biodegradable waste etc), representing a paramount opportunity
for future developments of a “sustainable” biofuel industry..
There is no unique production process to transform feedstock and raw materials
into biofuels, as to date there are different pathways: some of them are well
established, while others are still in early stages of their development,
needing further time and investments in R&D in order to achieve economic and
commercial readiness. A brief overview of some of current and potential pathways
is hereby presented (source: UK DfT)2:
o Biodiesel can be produced from a variety of vegetable oil feedstock such as
rapeseed oil, soybean oil and sunflower oil. Rapeseed currently accounts for
over 80% of global biodiesel production, while sunflower oil accounts for 13%.
The process starts with oilseeds being crushed to produce oil, which after
filtering is mixed with ethanol or methanol. The resultant esterification
reaction produces fatty acid methyl esters, which are the basis for biodiesel.
The technology for extracting oil from oilseeds has remained the same for the
last 10-15 years and is not likely to change significantly. Similarly, biodiesel
production from the oil is a relatively simple process and so there is little
potential for efficiency improvement. Research is underway as to improving the
utilization of co-products.
o Bioethanol can be produced by wood and straw, using acid hydrolysis and enzyme
fermentation. This process is technically feasible but is complex and expensive
and there are few industrial examples. Ongoing research and development in the
US aims to address cost issues and develop a more efficient process. This is
thought by many to be a step on the way to the eventual goal of an enzyme
hydrolysis process.
o Bioethanol from wheat from malting and fermentation provides for a similar
process to that for other methods producing bioethanol by fermentation, but an
initial milling and malting (hydrolysis) process is necessary. The wheat is
first crushed or milled. In its passive form, malting is a process by which
under controlled conditions of temperature and humidity, enzymes present in the
wheat break down starches into sugars.
o Bioethanol from corn using fermentation is similar to the process for wheat,
but with small differences in the initial processing of the corn. Firstly, the
corn must be milled, either by wet milling or dry milling. The milling produces
co-products of residues which can be sold as animal feed. Enzymes are used to
break down the starches in the corn into sugars which are then fermented and
distilled using the same process as for wheat.
o Bioethanol from sugar cane or sugar beet using fermentation is probably the
simplest of all the processes for producing bioethanol by fermentation. The
harvested sugar cane or sugar beet is crushed and then soluble sugars are
extracted by washing through with water.
o In perspective, biodiesel from wood or straw might be produced by using
gasification and Fischer- Tropsch process. First pioneered for the purpose of
converting solid fuels, mainly coal to liquid fuels, in countries where there
was a very limited indigenous supply of oil, it starts up with the gasification
of the feedstock to a "synthesis gas", which is primarily a mixture of hydrogen
and carbon monoxide. This gas can, in turn, be converted to liquid fuel in the
Fischer-Tropsch reactor, which makes use of a catalyst (usually iron-based). The
reactor also produces significant heat which can be used to generate electricity
as a significant co-product of the process. There is little information in the
literature about Fischer-Tropsch processing of biofuels, although the process
should be very similar to the fossil fuel process. The key challenge for
biofuels is to adapt and optimize the whole system to a scale that is
appropriate to the availability of the biomass feedstock.
o Bioethanol from wood or straw could be produced by enzyme hydrolysis and
fermentation. Even if this process is not yet developed enough to be put into
practice, it is expected to be commercially viable by 2020. It is essentially
similar to the process in which ethanol is produced from wood and straw through
acid hydrolysis and fermentation, except that enzymes instead of acids are used
for the hydrolysis process.
Environmental benefits of biofuels
The use of biomass energy has many unique qualities that provide environmental
benefits. It can help mitigate climate change, reduce acid rain, soil erosion,
water pollution and pressure on landfills, provide wildlife habitat, and help
maintain forest health through better management.
> Biofuels have a number of advantages over conventional fuels. First and
foremost, they come from a renewable resource; moreover, GHG emissions will be
reduced as the fuel crops absorb the CO2 they emit through growing.
> The use of ethanol-blended fuels as E-85 (85% ethanol and 15% unleaded
gasoline) can reduce the net emissions of GHG up to 25%, thanks to carbon
sequestration during corn farming, which more than offsets GHG emissions during
corn farming and ethanol production. Ethanol-blended fuel as E-10 can reduce GHG
up to 3.9%3.
> B20 bio-diesel reduced total hydrocarbons by up to 30%, Carbon Monoxide up to
20%, and total particulate matter up to 15%4.
> Biodiesel reduces emissions of carbon monoxide (CO) by approximately 50 % and
carbon dioxide by 78 % on a net lifecycle basis because the carbon in biodiesel
emissions is recycled from carbon that was already in the atmosphere, rather
than being new carbon from petroleum that was sequestered in the earth's crust.
(Sheehan, 1998)5
> Farrell et al. (2006) estimate that the fuel cycle for energy from grain
ethanol requires up to 95% less petroleum than the fuel cycle for an equivalent
amount of energy from gasoline6
> A study by the US Department of Energy has found that bio-diesel production
and use, in comparison to petroleum diesel, produces 78.5% less CO2 emissions7
> The following figure from EPA studies shows how biodiesels are less harmful on
the environment from the point of view of emissions8
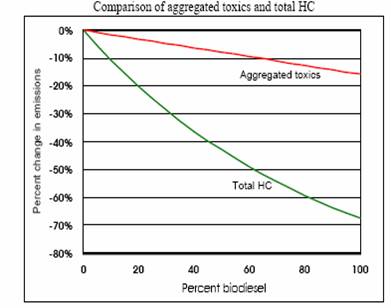
> Biodiesel helps to preserve and protect natural resources. For
every one unit of energy needed to produce biodiesel, 3.24 units of energy are
gained. This is the highest energy balance of any fuel.
> Biodiesel is nontoxic and biodegradable. Tests sponsored by the United States
Department of Agriculture confirm that biodiesel is ten times less toxic than
table salt and biodegrades as fast as dextrose (a test sugar)
> Some studies, scuh as the WRI’s9,
highlight a sort of trade/off between different environmental effects: an
increase in the production of biofuels, namely ethanol, will have different
impacts according to the environmental issue we take into account (for further
information and details on the study, please visit
http://pdf.wri.org/beyondrfs.pdf ):
|
Ethanol production may be a promising
technology to reduce GHG emissions from the production and use of
transportation fuels, as well as to diversify the nation’s liquid
fuel supply. Our study predicts that such a strategy will also have
a positive impact on aggregate farm income and result in significant
reductions in farm support payments. Given current grain-based
ethanol technology and in the absence of policy intervention,
however, these benefits will come at a cost to our nation’s water
and soil health. An expanded ethanol market is likely to provide an
incentive for farmers to revert to more intensively managed
rotations and less sustainable management practices, which may have
long-term implications for soil and water quality. |
However, there is no general agreement whether bio-fuels are actually less
“polluting” than petro-fuels, if we take a broader perspective. For example,
global warming pollution savings from biofuels can vary substantially depending
on crop growth techniques and pathways, and that is the reason why there are
many ongoing activities in such direction, like Environmental Defense Fund
working with farmers and commodities groups to develop a low-carbon
certification program for biofuels. Moreover, there are many complex
interactions and overlapping so that an improvement in a given indicator might
imply a worsening of another, with a trade off whose overall balance is
difficult to assess.
If we look at the following figure, we note how while there are considerable
advantages in terms of reduced greenhouse gas emissions, there are also
disadvantages due to the contribution to acidification and eutrophication (SRU
2005).

Last but not least, we have to keep in mind that it is not only the fuel itself
that has to be taken into account, but all the production and consumption
process as a whole.
We have seen how an argument used to support ethanol as a "green" fuel is
actually that it is renewable, and that by burning it as transportation fuel the
carbon dioxide thus released is absorbed by the plants from which the
alternative fuel is produced. From such perspective, fuel ethanol consumption
could be considered CO2 neutral. However, GHG debits arise during the whole
process of crop production to consumption, due to the use of agricultural
chemicals, fuelling of farm machinery, transportation activities, crop
processing and so on. All this obviously involves the use of fossil fuels (and
hence GHG emissions), and the same goes for the net energy value of ethanol,
where results are very much dependant on the nature of the feedstock and the
source of power used for the production process.
This skepticism will be better addresses in the next section, taking into
account all the pillars of sustainable development and hence focusing also on
other dimensions such as the social one.
Can biofuel development lead to “competition for land” and other
backlashes?
There is indeed an ongoing discussion on whether an increase in biofuel
production might impact upon land-use patterns and deforestation, undermining
availability of food and leading to a harsh competition for land. By diverting
agricultural production away from food crops, energy crop programmes are feared
to “compete” with food crops in a number of ways, ranging from the land use
itself to rural and infrastructure investments, from water and fertilizers use
to skilled labor, and so on. To date, there is actually no general agreement
upon the consequences of an intensive development of bio-fuel oriented crops. We
will briefly describe the rationale of “optimists” and “pessimists”, trying to
find some common ground and to stress some policy options that might be useful
to achieve broadly agreed-upon solutions that address environmental, social and
economic needs at once.
Pessimists:
First of all, we should stress that the problem linked to biofuels sector
development is multi-faceted, as there is the need to address many issues that
are deeply interrelated. Concerns range from the scarcity of available land that
might hinder food production to the possible exploitation of forest areas, with
subsequent damages for wildlife and bio-diversity at large; from an
unprecedented pressure on soil and water resources to the social consequences
that agro-energy giants development might bring to small farmers and
agricultural communities, and so on.
And such concerns are made even greater by the awareness that current
demographic trends will put an increased pressure on agriculture, as to
adequately feed a population that according to FAO figures is supposed to
increase by more than 3 billion by 2050. Given such framework, will it be viable,
from both a practical and ethical point of view, to set aside part of arable
lands for biofuels?
Human society is already farming about 37 % of the global land area, and using
almost all of the good-quality land. Additional farmland will have to come at
the expense of forest and wild species, and is likely to incur heavy penalties
in terms of soil erosion, drought risks, and endangered wild species (Avery
2006). As a matter of fact, if present arable land won’t be sufficient to
address the need of land for biofuel oriented agriculture, producers will
inevitably turn to areas that are nowadays unexploited due to their poor quality
from an agricultural perspective.
However, many studies stress that land too poor to farm has contained virtually
all of the world’s wildlife species from time immemorial, while on the other
hand best croplands never had many wild species. For instance, a national park
in the Peruvian Amazon contains more than 1,300 plant species, 332 bird species,
131 species of amphibians and reptiles, 70 different species of non-flying
mammals, plus thousands of species of insects, and a few square miles of
tropical forests may contain more above-ground species than all of North
America. Expanding fuel crops onto poorer-quality land might therefore take a
devastating toll on wild species displaced or lost (Avery 2006).
Indeed, this is consistent with the concerns emerging from a recent research
carried out by the Worldwatch Institute. Not only it raised the concern that if
fuel crops are grown on ecologically fragile lands, this might accelerate soil
erosion and the depletion of aquifers; but also, biofuel crops could have
negative impacts on local ecosystems and biodiversity, as “ecologists point with
alarm to the massive Brazilian soybean crop that is encroaching on the outer
fringes of the Amazon Basin”.
Worldwide, during the last decade per capita available cropland decreased 20%
and irrigation 12% (Brown 1997)10.
Indeed, Agricultural water use is a serious concern not only in developing
countries, but also throughout Europe and especially in southern parts of the
continent; according to the EEA, in such areas water availability is low and
varies from year to year, and increases in irrigated land have contributed to
water scarcity, with the lowering of water tables and water levels in rivers and
lakes. To use EEA words, “the substantial rise in the use of biomass from
agriculture, forestry and waste for producing energy might put additional
pressure on farmland and forest biodiversity as well as on soil and water
resources”.
As suggested before, the booming of biofuels might have negative repercussions
not only for the natural environment and for the stock of food available, but
also as far as economic and social dimensions are concerned. Warnings in such
direction are being given by many organizations, such as Planet Ark: its
analysis on the issue stresses how the mushrooming of mono-crops for bio-fuels
around the globe, through raising the risk of greater competition for land and
feedstock, is actually threatening to lift prices of both bio-fuels and food.
The large-scale promotion of bio-energy relying on intensive cash crop
monocultures could lead for instance to a sector dominated by a few agro-energy
giants, without any significant gains for small farmers. There is hence little
doubt that good planning will be needed to prevent the competition for land
between energy and food crops.
Here is some other data highlighting how competition for land might be on the
horizon, if biofuel production is to be increased, at current efficiency
patterns:
• The grain that could feed a person for one year is required just to fill the
petrol tank of a Range Rover (McNeely)11
• Given current road transport consumption in the UK (around 37.6m tonnes of
petroleum products a year), a shift towards biofuels in the modest target of 20%
by 2020 would not be sustainable in the near future. A production of biofuel
based on rapeseed, the most productive oil crop to be grown in the UK, would
consume almost all available 5.7m hectares cropland (Monbiot, 2004)12.
If the same thing is to happen all over Europe, the impact on global food supply
will be catastrophic so that the net balance would tip from net surplus to net
deficit. If, as some environmentalists demand, it is to happen worldwide, then
most of the arable surface of the planet will be deployed to produce food for
cars, not people.
• Many believe that there is a sort of trade off between nature conservation and
biofuels. The following figure, for instance, represents the crop coverage
needed to meet the EU 2010 target of 5,75% biofuel13
:
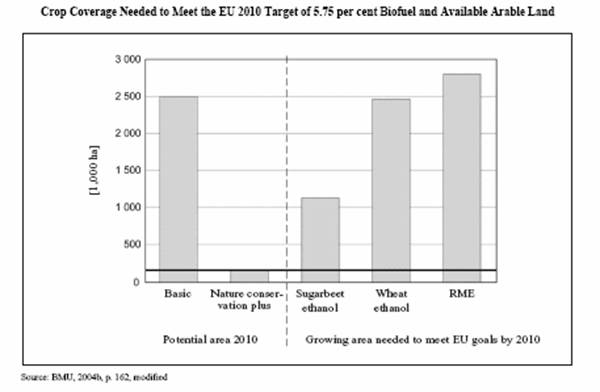
In the “Basic”
Scenario the minimum requirements of nature conservation law are meant to be
taken into account, while in the Nature Conservation Plus Scenario nature
conservation requirements receive greater consideration.
If we are to manage land according to current sustainability standards such as
in the Nature Conservation Plus Scenario, the EU target would be missed by a
wide margin. Instead of the 5.75% fuel share, this variant would produce 0.78%
sugar beet and ethanol, 0.35% wheat and ethanol and 0.31% biodiesel, being this
represented by the line in the figure.
• It is feared that meeting a relevant increase in biofuels demand in areas such
as the EU and the USA using conventional crops such as grain, sugar or oil seed
crops might require a vast allocation of cropland, as shown by the following
table (IEA 2004):
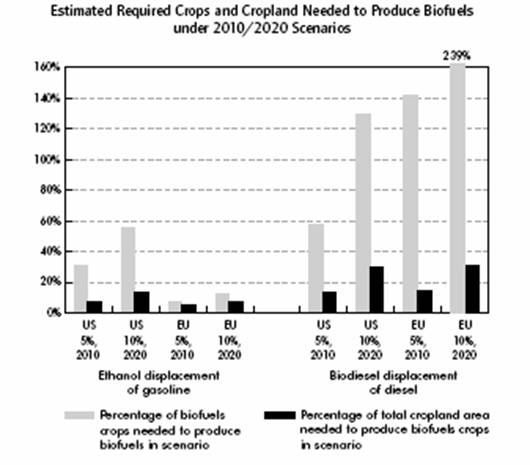
• Contrarily to what generally agreed upon, some believe that
biofuels have a very poor energy balance. Moreover, in some cases such as corn
ethanol, the fuel would be actually produced at an actual net energy loss.
Another case is that of soybeans:14
an acre of U.S. soybeans is worth only 52 gallons of biodiesel per year. Each
soybean acre produces only 40 bushels of soybeans, or one-third the grain yield
of corn. Each bushel of soybeans produces 1.4 gallons of biodiesel, with 93% of
diesel’s energy.
• As regards for instance corn grown in the US, we can note from the following
figures that while the yield itself is very abundant, the overall energy balance
is pretty poor, if compared to other crops such as sugar cane15
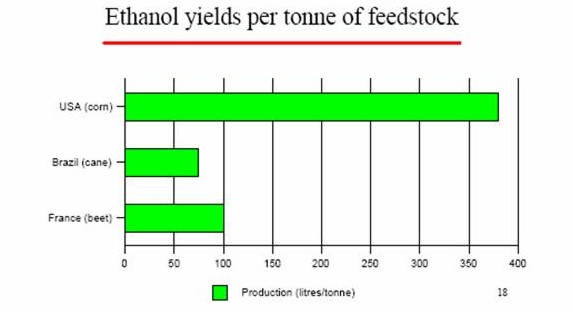
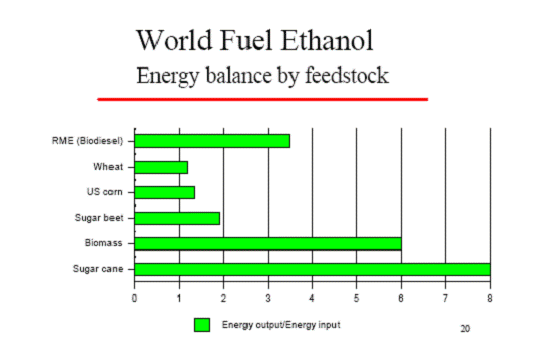
• Pimentel16 affirms that producing ethanol from US corn actually displays a negative energy balance, as “about 29% more energy is required to produce a gallon of ethanol than the energy that actually is in the gallon of ethanol produced”:
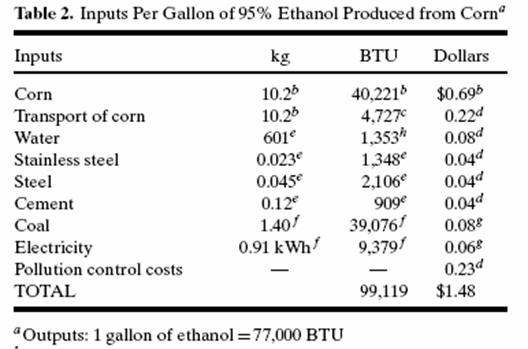
• The point is that when all of the elements required to produce
biomass-based liquid fuels such as ethanol and biodiesel are added together, the
energy requirements for production far exceed the energy produced.
...corn requires 29% more fossil energy than the fuel produced; [...] soybean
plants requires 27% more fossil energy than the fuel produced [...]17
In assessing inputs, the researchers considered such factors as the energy
used in producing the crop (including production of pesticides and fertilizer,
running farm machinery and irrigating, grinding and transporting the crop) and
in fermenting/distilling the ethanol from the water mix.
• This is consistent with the conclusions drawn by McNeely: due to the use of
fossil fuels at every stage of the production process (from cultivating to
processing and transporting), growing maize appears to use 30% more energy than
the finished fuel produces. Moreover, McNeely states that using ethanol rather
than petrol reduces total CO2 emissions by only 13%, because of the pollution
caused by the production process.
• Projected world power requirements in 2052 will rise to a total of 22 to 42
trillion watt-hours (Avery 2006). Producing this from crops could require as
much as 80% of the Earth’s total land area, so that we would need to be
energy-cropping areas such as the Gobi Desert, the Amazon River basin or even
northern Siberia.
• Credit Suisse says that a rise in global bio-diesel share to two percent of
the total amount of diesel used in transportation would completely deplete
current vegetable oil stocks, and arable land that would otherwise have been
used to grow food would instead be used to grow fuel (Exchange Magazine, 2006).
Optimists
On the other hand, there are other voices that are skeptical about the possible
detrimental consequences of bio-fuels for arable land and food stocks, and for
sustainable development at large. This large party believes that biofuel is the
solution and not the problem.
First of all, there is evidence that world population is of course growing, but
at a decreasing rate, and such trend will continue in the next decades so that
global population should stabilize somewhere around the middle of the 21st
century.
The following figures, taken from UN “The World at six billion”, clearly show
how, even if global population is still in the increase, the trend has changed
as growth rates are rapidly declining:
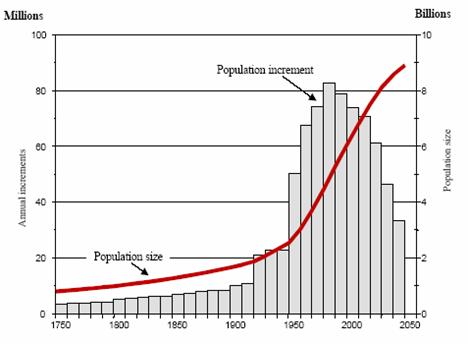
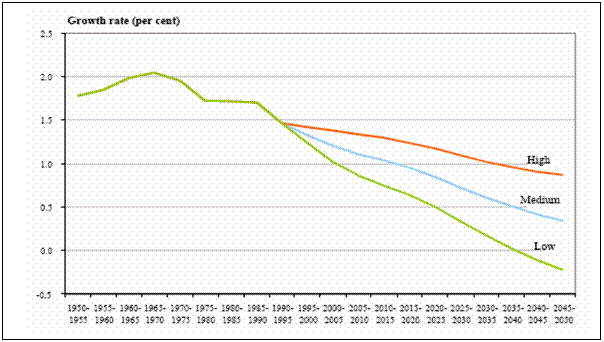
Moreover, it appears that the world is not “running out of food”. Even in the
scenario of an increased population, there would still be room to divert some of
the production towards biofuels.
This so-called 'food versus fuel' controversy appears to have been exaggerated
in many cases, as the world's real food situation displays an ever-increasing
food surplus in most industrialized and a number of developing countries.
We can consider for instance food shortages experienced by Brazil a few years
ago. The blame had been put on the ProAlcool programme (fuel ethanol), but a
closer examination does not support the view that bioethanol production
adversely affected food production. Brazilian agricultural production has always
kept ahead of population growth: in 1976 the production of cereals was 416 kg
per capita, and in 1987 -- 418 kg per capita. Of the 55 million ha of land area
devoted to primary food crops, only 4.1 million ha (7.5 per cent) was used for
sugarcane, which represents only 0.6 per cent of the total area registered for
economic use (or 0.3 per cent of Brazil's total area). Of this, only 1.7 million
ha was used for ethanol production, so competition between food and crops is not
significant.
The world already grows more than enough food to feed everyone. Yet about a
billion people still don't have enough food to meet basic daily needs. There is
more food per capita now than there's ever been before. It is the inequitable
economic system, and not overall food scarcity, that should be held accountable.
The following table is taken from 12 Myths about hunger18:
|
Myth 1: Not Enough Food to Go Around
Reality: Abundance, not
scarcity, best describes the world's food supply. Enough wheat, rice
and other grains are produced to provide every human being with
3,500 calories a day. That doesn't even count many other commonly
eaten foods - vegetables, beans, nuts, root crops, fruits, grass-fed
meats, and fish. Enough food is available to provide at least 4.3
pounds of food per person a day worldwide: two and half pounds of
grain, beans and nuts, about a pound of fruits and vegetables, and
nearly another pound of meat, milk and eggs-enough to make most
people fat! The problem is that many people are too poor to buy
readily available food. Even most "hungry countries" have enough
food for all their people right now. Many are net exporters of food
and other agricultural products. |
As far as the energy balance is concerned, many believe that advances in technology have improved production efficiency, giving all current biofuels a positive fossil energy balance. Not only is the efficiency of the conversion process advancing steadily, but bioenergy is increasingly being used for feedstock processing as well. Both approaches reduce the amount of fossil fuels used to convert crops into biofuels. (Wordlwatch Institute 2006):
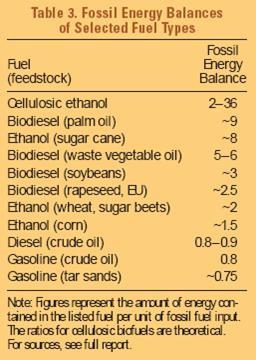
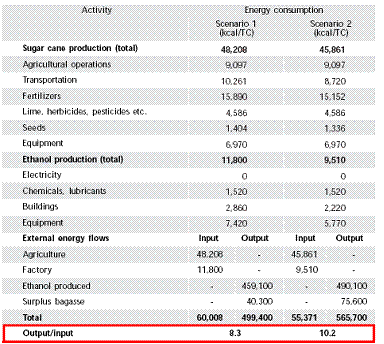
We can take a closer look of the energy balance of biofuel by focusing on a
specific case, such as that of sugarcane ethanol in brazil: the following figure
shows as, even taking into account all the energy used during the process, the
output/input ratio is overwhelmingly positive, being around 8,3 or more
depending on the assumptions that are beneath the calculations (Coelho 2005).
The question that most
researchers ask themselves is “how much fuel can we grow? How much land will it
take?”. There is widespread fascination with high yielding oil crops,
particularly oil-bearing algae, with oil palms running second. It seems obvious
that the highest-yielding crops will produce the most energy from the least
amount of land. But high yield is not the only factor in farming, and it may not
always be the most important factor. It can make more sense for a farmer to grow
a lower-yielding crop if it has more useful by-products or requires fewer inputs
or less labor or it fixes more soil nitrogen for fertilizer or it fits a crop
rotation better.
The challenge would therefore be that of increasing substantially the production
of bio-fuels by using innovative feedstock, processes and technologies, which
are both competitive and sustainable. Also, we have to keep in mind that
agricultural and forestry systems currently exploit only part of their
production, i.e. “primary” products, while they leave unexploited significant
“residual” quantities. Hence, the use of both the primary and the residual
resources through integrated and sustainable pathways should be promoted.
Bridging the gap
In seeking to bridge the large gap between the optimists and pessimists, there
may be some common ground on high-yielding oil crops, particularly oil-bearing
algae, with oil palms running second. It seems obvious that the highest-yielding
crops will produce the most energy from the least amount of land. Indeed, we
have to note that the yields of a given crop can vary extremely significantly,
due to a number of reasons ranging from the quality and the geographical
position of the land, to the type of pesticides and fertilizers used (if any),
from the irrigation system to the eventual genetic modification, and so on.
If we consider for example the fertilizer issue, it should be stressed that
strategies differ significantly around the globe. There are areas where a little
amount is more than enough to secure high crop yields, while elsewhere (such in
Brazil) most arable lands must be intensively fertilized, as this is vital for
key crops like sugarcane and soybeans19.
Planning efforts should therefore focus on choosing the best available cropping
solutions for each region and land type. The following table summarizes the
yield ranges from some Italian crops suitable for biofuel production20.
|
|
Crop Yields (t/ha) |
Energy Output (Gj/ha) |
||
|
|
min |
max |
min |
max |
|
Wheat |
1,27 |
6,46 |
12,1 |
63,6 |
|
Barley |
1,26 |
6,21 |
10,8 |
57,1 |
|
Corn |
3,18 |
12,25 |
31,8 |
124,6 |
|
Sorghum |
2,02 |
8,73 |
18,9 |
84,5 |
|
Beet |
34,45 |
66,36 |
72,3 |
171,4 |
And the same goes for
crops grown in developing countries, where the yields vary significantly as
different factors (rainfall, soil acidity etc) play a relevant role. The
following picture shows the stem yields of sweet sorghum in different Zambia
sites:
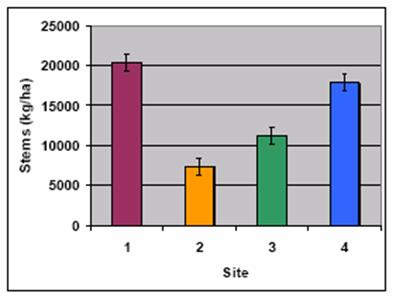
Given the broadness of
such ranges, it becomes of paramount importance to achieve a high efficiency in
cropping techniques, so that a relatively small area of arable land will provide
a fair amount of biofuels.
Not only traditional crops should be taken into account, as the future of
biofuel might be linked to the exploitation of “new” plants such as the jatropha,
very common in India and expanding in some African areas. Jatropha is
particularly interesting as it establishes itself easily even in arid and waste
land (areas with rainfall as low as 200mm per year ), where other crops would
perish (and such land is often abundant in the poorest areas of the developing
world). Jatropha plants produce seeds with an oil content of 37%, but there are
also reports of getting oil yield as high as 50% from the seed (PCRA data). The
oil can be combusted as fuel without being refined. It burns with clear
smoke-free flame, and has been tested successfully as fuel for simple diesel
engine. Moreover, the oil also contains insecticide which can be used as a
rewarding byproduct21.
However, jatropha yields vary significantly, as seed production ranges from
about 2 to over 12.5 t/ha/year, depending on many factors such as low and high
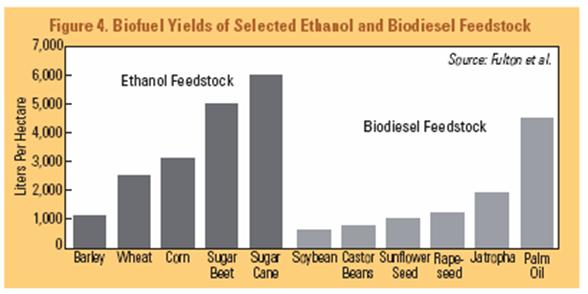
rainfall areas. If we consider average yields, we note that Jatropha has better
yields than all other biodiesel feedstock, with exception of palm oil (Worldwatch
Institute 2006).
Other studies evidence an even better performance of Jatropha Curcas:
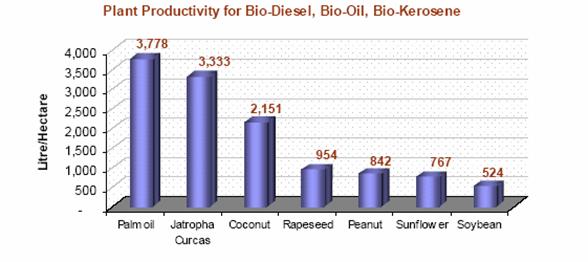
Some further
advantages of this plant are listed below:22
> Jatropha is a drought resistant perennial living up to 50 years.
The tree grows up to a height of 3 meters, which means harvesting is an easy
task.
> It takes two years for a 'Jatropha' sapling to begin producing seeds, and they
can produce seeds for up to 40 years.
> The plant is not exploited or damaged by animals and birds.
> Jatropha holds promise for rural prosperity to the farmers, farm-labourers and
women in terms of employment and income generation.
> Jatropha adds richness to the environment by abating carbon, alleviating
pollution, conserving oil and preventing soil erosion and desertification.
> The residue obtained after removing oil from seed is used as a fertilizer for
erosion soil.
If we focus on India, we notice how the country has 60 million hectares of waste
land, of which it is estimated that half might be used for Jatropha
cultivation (IFPRI 2006).
The cost of producing biodiesel from Jatropha is between US$0.43 and US$0.54 per
liter (IFPRI 2006). In order to exploit such great potential, in February 2006
the Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) of India announced to be about to
undertake a 10-year project, in conjunction with BP, to cultivate 8,000 hectares
of wasteland with Jatropha and install the equipment necessary to produce 9
million liters of biodiesel a year. Also, the project pledges to include a
thorough analysis of the social and environmental impacts of the approach.
However, Jatropha has also some disadvantages, which can be briefly outlined as
follows:23
1. The energy ratio (output/input) of 1.5 is low compared to
other energy sources, but is still higher than other biodiesel sources.
2. This shrub is not frost-resistant.
3. Outputs from crops can widely vary, from less than 1 ton per hectare to 6
tons.
Moreover, due to several different toxic principles including a lectin (curcin),
phorbol esters, saponins, protease inhibitors and phytates, neither the seeds
nor the press cake nor the oil of Jatropha curcas can be used for human or
animal nutrition; even if the plant is not intended for human consumption, its
toxicity might represent a problem, especially if grown in areas close to food
crops plantations24
While many biofuel critics point the finger at the extensive agricultural
resources needed to produce a gallon of fuel, we should remember that the
technology is still in its infancy. The petrochemical industry had about a
half-century head start, so it is not surprising that gasoline is more efficient
now. However, there are ongoing efforts to increase crop yields, this being the
winning strategy to achieve a synergic between environmental and economic
efficiency (for example, companies such as DuPont and Monsanto are learning how
to optimize crop yields for ethanol and biodiesel production).
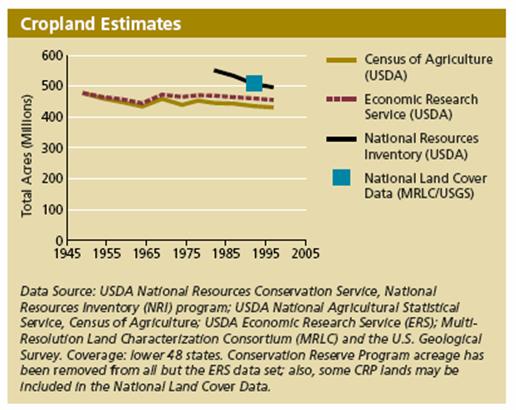
The following figures illustrate the steady improvements in US crop yields over
the past 50 years25:
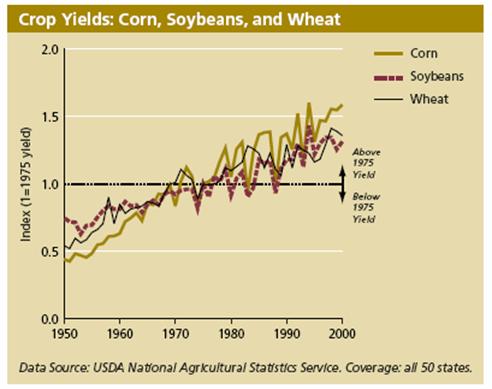
Increasing the amount of food grown per acre has allowed U.S. agriculture to
produce more food and fiber without corresponding increases in farm acreage. The
total acreage used for agricultural production has declined slightly over the
past half-century.
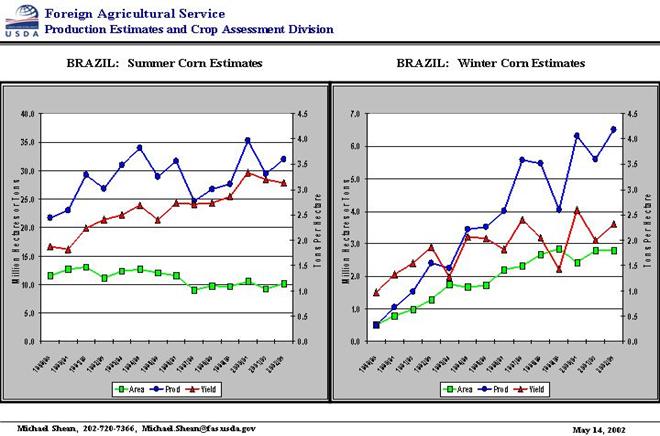
This increasing trend
is typical of most regions, and not only the US. We note from the following
figure that even Brazil has experienced an increase in crop yields over the past
decades.
Next we present some data showing how both crop yields and conversion yields are
improving, and are expected to maintain these trends in decades to come26:
■ The average yield for corn in the US has increased from 5.7 to 7.9 metric
tonnes per hectare over the last 15 years (about 2% per year).
■ The USDA projects that corn yields per hectare will improve by another 10%
over the next ten years, and that soy yields will improve by about 5%.
■ Between 1975 and 2000, sugarcane yields in the Brazilian São Paulo region rose
by 33%, ethanol production per unit of sucrose rose by 14%, and the productivity
of the fermentation process rose by 130% (IFPRI 2006)27.
■ Conversion yields are also assumed to improve, at about 1% per year for
ethanol (litres per tonne of feedstock), and at a slower rate (0.3%) for
biodiesel, since the process of crushing oil-seeds and converting to methyl
ester (biodiesel) is not likely to benefit as much from technological
improvements or scale increases (USDA, 2002; IEA, 2000a).
Efficiency in crop yields, besides traditional expedients such as tailoring the
crop rotation to the specificities of the arable area or optimizing irrigation/fertilization
procedures, will be gained through seed hybridization as well as through genetic
modification, obviously scrutinized for all of the potential health
ramifications.
Once again, we have to point out as there is no general agreement over the real
desirability of such efforts, as many fear that the outcome of twisting natural
laws might be unpredictable. For instance, the Swiss biotech firm Syngenta is
developing a genetically engineered maize that can help convert itself into
ethanol by growing a particular enzyme. Other companies are designing trees that
have less lignin, the strength-giving substance that enables them to stand
upright, but makes it more difficult to convert the tree's cellulose into
ethanol. Some environmentalists are worried that these altered trees will
cross-breed with wild trees, resulting in a drooping forest rather than one that
stands tall and produces useful timber and wildlife habitat28.
Moreover, there is some concern that genetically modified products are not
suitable for human consumption. It would be therefore very difficult to avoid
and control eventual cross breeding, which might occur not only by tampering
attempts, but also by simple natural phenomenon such as wind transferring seeds
for hundreds of miles.
The Brazilian case: among successes and challenges
The Brazilian case is a success story which is often used to characterize the
biofuel industry; however, we will point out some flaws that are still hindering
the achievement of a truly sustainable scenario.
The use of ethanol to fuel automobiles was initiated partially in response to
the oil shock of 1973, and as an alternative to oil to promote self-sufficiency.
In 1975, the government created the Brazilian National Alcohol Program to
regulate the ethanol market and encourage the production and use of fuel ethanol.
The program guaranteed that all gasoline sold in the country would be blended
with 22% anhydrous ethanol and that the pump price would remain competitive with
gasoline. Past sugarcane crop problems have slightly altered the percentage of
ethanol in Brazilian gasoline, however, mandated levels have usually remained at
around 20%. The program successfully reduced by 10 million the number of cars
running on gasoline in Brazil, thereby reducing the country's dependence on oil
imports.
The following table summarizes the ethanol production process from sugarcane:
|
Sugarcane is harvested manually or mechanically and shipped to a processing plant, which is typically owned and run by big farms. There the cane is roller-pressed to extract the juice (garapa), leaving behind a fibrous residue (bagasse). The juice is fermented by yeasts which break down the sucrose into CO2 and ethanol. The resulting "wine" is distilled, yielding hydrated ethanol (5% water by volume) and "fusel oil". The acidic residue of the distillation (vinhoto) is neutralized with lime and sold as fertilizer. The hydrated ethanol may be sold as is (for ethanol cars) or be dehydrated and used as a gasoline additive (for gasohol cars).
|
The alcohol industry, entirely private, has invested heavily in crop improvement
and agricultural techniques over the past decades. As a result, average yearly
ethanol yield increased steadily from 300 to 550 m³/km² between 1978 and 2000,
or about 3.5% per year.
The following data apply to the 2003/2004 season29.
|
land use: |
45,000 km² in 2000 |
|
labour: |
1 million jobs (50% farming, 50% processing) |
|
sugarcane: |
344 million metric tonnes (50% sugar, 50% alcohol) |
|
sugar: |
23 million tonnes (30% is exported) |
|
ethanol: |
14 million m³ (7.5 anhydrous, 6.5 hydrated; 2.4% is exported) |
|
dry bagasse: |
50 million tones |
|
electricity: |
1350 MW (1200 for self use, 150 sold to utilities) in 2001 |
Ethanol-only cars were sold in Brazil in significant numbers between 1980 and
1995; between 1983 and 1988, they accounted for over 90% of the sales. 80% of
the cars produced in Brazil in 2005 were dual-fuel, compared to only 17% in
2004.
Domestic demand for alcohol grew between 1982 and 1998 from 11,000 to 33,000
cubic metres per day, and has remained roughly constant since then. In 1989 more
than 90% of the production was used by ethanol-only cars; today that has reduced
to about 40%, the remaining 60% being used with gasoline in gasohol-only cars.
Both the total consumption of ethanol and the ethanol/gasohol ratio are expected
to increase again with deployment of dual-fuel cars.
The improvement in air quality in big cities in the 1980s, following the
widespread use of ethanol as car fuel, was widely evident; as was the
degradation that followed the partial return to gasoline in the 1990s.
If we were to point out the most relevant policies that spurred Brazil’s success
in the biofuel industry, we should mention a broad set of factors ranging from
requirements for the industry to produce cars using neat or blended biofuels to
the subsidies for biofuels during initial market development; from the opening
of the electricity market to renewable energy–based independent power producers
in competition with traditional utilities to the support for private ownership
of sugar mills, helping guarantee efficient operations, and so on (stimulation
of rural activities based on biomass energy to increase employment in rural
areas, etc).
There is evidence (IFPRI 2006) that in 1997 the ethanol sector employed about 1
million people in Brazil. While 35% of these jobs were temporary harvesting jobs
employing many poor migrant laborers from the Northeast, 65% were permanent.
Moreover, 300,000 people found an occupation thanks to jobs created indirectly
by the ethanol industry.
Being most of these jobs simple and unskilled, the new situation created an
opportunity for many poor rural people, and rural farmers took advantage of the
situation, as well, since some 60,000 small farmers produce about 30% of the
sugarcane in Brazil (even if, as pointed out later, there is no general
agreement upon the actual benefits of the ethanol program for rural communities)
However, the ethanol program also brought a host of environmental and social
problems of its own. Sugarcane fields were traditionally burned just before
harvest and thus, the air pollution which was removed from big cities was merely
transferred to the rural areas.
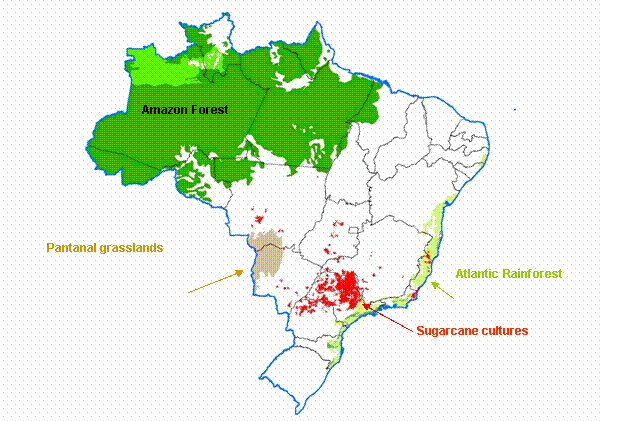
There is also widespread concern that the so-called soybean frontier is
approaching the rainforests, meaning this that the Amazon and other green areas
of Brazil are threatened by the rise in the cultivation of soybean for fuel
purposes, which might lead to deforestation in order to obtain more arable land.
And the same goes for sugarcane cultures, even if many point out how these
cultures are developing in areas that are far away from the Amazon region, thus
not representing a threat to rainforest habitat30:
A peculiar solution
suggested by some31
is that “the rest of the world to pay them to leave their trees intact”. In
other words, “avoided deforestation” should be included in a list of
emissions-reducing activities that rich countries can sponsor to help meet
obligations under the Kyoto protocol.
The International Institute for Environment and Development, has estimated that
logging, and the subsequent use of the land cleared each year, in eight forested
countries, would bring in $5 billion over a 30-year period. That translates into
a benefit of $3.50 for every tonne of carbon dioxide released. So far rich
countries have paid an average of $7 per tonne to reduce emissions in the
developing world, under the Kyoto protocol. At that rate they could pay
deforesters twice as much to leave trees alone as the latter get now for cutting
them down.
It should be noted that some other nations are better addressing the issue,
producing alcohol fuel with little harm on the environment thanks to
advancements in fertilizers and natural pesticides that is eliminating the need
to burn fields. And, thanks to condensed agriculture like hydroponics and
greenhouses, less land is used to grow more crops.
As far as social implications are concerned, many detractors of the biofuel
oriented policy affirm that the ethanol program led to widespread replacement of
small farms and varied agriculture by vast seas of sugarcane monoculture. The
consequence was a decrease in biodiversity and further shrinkage of the residual
native forests (not only from deforestation but also through fires caused by the
burning of adjoining fields). Moreover, the replacement of food crops by the
more lucrative sugarcane caused a sharp increase in food prices over the last
decade.
From the occupational point of view, since sugarcane only requires hand labor at
harvest time, this shift also created a large population of destitute migrant
workers who can only find temporary employment as cane cutters.
However, we should not overestimate the relevance of problems connected to
biofuel production in Brazil. While some doomsayers believe that sugarcane
cultivation will displace other crops, thus causing food shortages, we have to
stress how these concerns seem to be groundless. Despite having the world's
largest sugarcane crop, the 45,000 km² Brazil currently devotes to sugarcane
production amount to only about 0,5% of its total land area of some 8.5 million
km². In addition, the country has more unused potential cropland than any other
nation32.
Spurring biofuels: an overview on current policy options
To date, many organizations and bodies are addressing the issue of biofuels
development, both at national and international level. The United Nations
Development Programme (UNDP) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO),
the World Bank and the International Energy Agency (IEA) are all active in
supporting biofuels worldwide.
International cooperation is obviously to play a crucial role, if relevant
results are to be achieved. We can mention for instance the Horizontal Technical
Cooperation Program in agro-energy and bio-fuels, involving Brazil and other
countries of the Americas, whose aims are assisting countries in Latin America
and the Caribbean in developing agro-energy, generating employment and income,
complying with environmental policy and bringing such countries to the forefront
of the world’s biofuel industry.
Aware of the disputes over the effective eco-friendliness of such products, and
conscious of the eventual backlashes that they might imply, we hereby highlight
the directions on which the efforts are underway.
There are different sets of policy options that might spur the production on
biofuels, overcoming the diffused skepticism on high production costs. Such
options can be either fiscal/monetary or normative, and can be categorized into
two types:
> Application incentives, supporting the sale, distribution and use of biofuels
> Production incentives, such as tax credits, grants and loans for biofuel
producers
The following table summarizes some of current government support measures for
Biofuels in selected countries33:
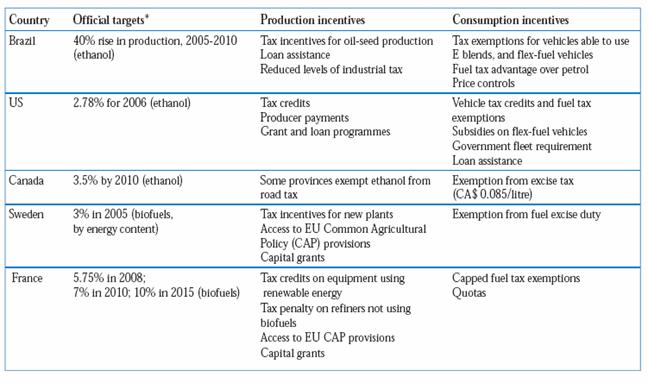
In a recent paper, Gururaja34 lists some policy options that are included in both the application and the production incentives sets:
|
-
Market mandates establishing blending norms for ethanol-gasoline and
biodiesel fuels; |
Particular attention
should be given to the efforts aimed at eliminating trade barriers, thus
facilitating international trade in biofuels. There is a great potential for
exports
from developing countries (such as Brazil, where ethanol costs are $0.1 to $ 0.2
cheaper than IEA countries) to developed ones, which might bring benefits to
both sides. Governments may hence consider building trade regimes applicable to
biofuels especially targeting the removal of trade barriers. Reforming the
tariff structure is the first step to adopt, in such direction, and
international cooperation will be needed to foster such process, and biofuel
trade at large.
The European Commission itself is devoted to bolstering the production and
uptake of biofuels The commitment is multi faceted, and efforts are to be made
in different directions35:
- Support biofuel demand (reference values are 2% of market share
in 2005 and 5,75% in 2010). Some Member States adopted imposing measures, so
that fuel supply companies must market a certain percentage of biofuels.
- Exploit environmental advantages. For instance, there is an ongoing discussion
viable paths of accounting biofuels in terms of CO2 emissions reduction
- Enhancing commercial opportunities. Namely, assessing the implications of a
possible distinctive trade code for biofuels. Besides, there is already an
ongoing liberalization process, given the Doha Round on one hand, where
bioethanol will undergo a tariff reduction, and the EU/Mercosur deal on free
trade on the other.
- Supporting developing countries. For instance, the EC is willing to support
developing economies in overcoming the hindrances they are facing after the
European sugar reform. On the basis of a case-by-case analysis of each country
specificities, this might encompass also directly supporting the production of
bioethanol.
- Supporting R&D, as the goal is that of abating costs by 30% by 2010, in the
wake of the success of past projects such as EUROBIODIESEL, and the promising
kickoff of new ones such as RENEW and NILE.
Also developing countries are addressing the issue of supporting biofuel
industry, and Tanzania is a case in point.36
The development of a strong biofuels sector in Tanzania will initially require
supportive policy pressure. We hereby list some of the measures suggested by the
study, encompassing both traditional and non-traditional policy approaches:
> Fuel Tax Incentives could bolster the use of biofuels, making them more
price-competitive with petroleum fuels. Fuel excise taxes represent a
significant percentage of the price Tanzanians pay for fuels, so that exempting
alternative fuels from part of such burden would be a powerful tool for
‘leveling the playing field’. Reduced government revenues could be avoided by
adjusting the taxes on all fuels, so that overall revenues remain constant.
> Carbon-based Fuel Taxes might support biofuels, as they tax the externality (carbon)
directly
> A CO2 emission trading system would cap the quantity of emissions allowed by
various emitters, and the right to emit becomes a tradable commodity.
> Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) consist of one country engaging in projects
through which an entity partially meets its domestic commitment to reduce GHG
levels by financing and supporting the development of a project in another
country.
> Governments can also implement fuel standards as a mechanism for altering the
transport sector fuel mix, setting a minimum fuel content of non-petroleum (or
renewable) fuel and hence using regulation to drive the market.
> Incentives for Investment into Biofuels Production Facilities are needed, as
required investment in commercial scale production facilities represents an
important barrier to the development of a biofuels market.
> Also, the focus is to be put on trade policies to remove barriers to
international biofuels trade. Biofuel production costs worldwide vary
significantly, and so does the production potential of different regions. It
therefore appears to be substantial potential benefits from international trade
in biofuels, but lacking specific rules, biofuels are generally subject to
customs, duties and taxes without any particular limits. The ethanol market in
several developed countries is strongly protected by high tariffs. However, we
should keep in mind that ethanol itself is part of a list of environmental
products for which accelerated dismantling of trade barriers is sought, so there
are some prospects for the eventual elimination of such tariffs. For Tanzania
and other developing countries, an initial protection of local manufacturers
(e.g. through import duties) against cheaper imports is necessary if the
build-up of a strong national biofuels industry is to be achieved.
We can conclude by mentioning the so called “Green OPEC”, an African
organization of biofuels producing and exporting countries where some of the
continent poorest nations are clubbing together to try to position themselves as
global suppliers of biofuel itself.
13 nations met in Senegal to form the Pan-African Non-Petroleum Producers
Association (PANPP), aimed at developing alternative energy sources, especially
biofuels.
As a matter of fact, Africa produces a range of crops that could be used to make
biofuel: these include sugar cane, sugar beet, maize, sorghum and cassava (suitable
for ethanol production) and peanuts, jatropha and palm oil (for the production
of biodiesel). Thus, turning to biofuels is considered by many as the only way
out of the threat of a permanent economic regression that might hit those areas
of the continent that lack crude reserves (especially in a period of soaring oil
prices), achieving at once national energy supply diversification, energy
security and on balance of payments thanks to the avoided costly outlays for
fuel imports.
Towards biofuels
certification
There is a growing concern regarding the need for biofuels to receive third
party, independent environmental certification, as current practice of
automatically classifying all biofuels as ‘renewable’ (regardless of how they
are produced) is counter-productive
That is, the industry needs a proof that not only biofuels are less harmful on
the environment than other traditional fuels, but also that the production
process itself is environment friendly from cradle to grave, and complying with
corporate environmental regulations.
Indeed, to date biofuels are facing many sustainability challenges, stemming
from structural agricultural components as employment and farm income issues to
chemical, fertilizer and fuel inputs impacting the overall energy balance of
different biofuel products. Various dematerializations and substitutions
throughout the life cycle of biofuel production and processing have been
progressing, however did not always go far enough. At the regional and local
level site selection and its effects on biodiversity, and local water quality,
are often of significant concern.
Biofuel certification could also be of vital importance for those organizations
(both private and public) willing to promote their “green” image with other
stakeholders and the public at large. Indeed, consumers turn to biofuels
trusting that by their choice they make a difference, contributing to the
reduction of their environmental footprint related to energy use. A
certification providing an assessment of biofuels value chain can be the key to
ensuring that this trust is well placed.
Not only environmental concerns are related to the setting up of biofuel
certification, as some fear, for instance, that this might be against WTO rules;
however, most analyses on the issue (such as that of law firm DLA Piper) advise
that, as long as the system is carefully designed so that it treats all market
players equally and is based on thorough consultation with all concerned, it
should be compatible37.
Today, there are no green labels specifically tailored to biofuels and assessing
their whole value chain, as the only type of certificate that exists is a
guarantee for a certain percentage of biofuel content in gasoline or diesel (Sustainable
biofuels program; White Paper 2006). However, there are plenty of activities
going on in the context of grey energy assessment and Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
of biofuel. We can mention, for instance, the completed EU-study by the Joint
Research Center (http://ies.jrc.cec.eu.int/wtw.html) as well as the ongoing SOFE
project (http://www.esu-services.ch/bioenergy.htm).
Biofuels can be produced in many different ways, from a large variety of crops
and feedstock. Depending on the technologies and processes used, biofuels can
have a positive or negative ecological and social impact, and a labeling/certification
process could provide some guidance and incentive for the increasingly growing
markets to develop in a “sustainable” way.
If we broaden the perspective, we note how to date there is a wide range of
initiatives and standards which, even if focusing on more “generic” issues as
the sustainability of “agriculture” and “forestry”, indirectly deal with the
eco-friendliness of biofuels.
As far as agriculture is concerned, we can mention for instance the Sustainable
Agriculture Network (SAN), a coalition of organizations promoting the
sustainability (both environmental and social) of agricultural activities by
developing a standard and certifying farms complying with it.
In 2005, SAN approved the final version of the standard, whose list of
principles is hereby presented as they apply to all crops, including of course
those providing biofuels feedstock38:
■ EMS
■ Ecosystem conservation
■ Wildlife protection
■ Water conservation
■ Fair treatment and good working conditions for workers
■ Occupational H&S
■ Community relations
■ Integrated crop management
■ Soil management and conservation
■ Integrated waste management
Also forestry
management is relevant for the sustainability of biofuels, as it both provides
feedstock for their production and “vital space” for fuel crops to be grown.
With forest certification an independent organization develops standards of good
forest management, and then independent auditors issue certificates stating that
forests are well-managed—as defined by a particular standard—and ensures that
certain products like biofuel feedstock come from responsibly managed forests.
To date there are several different systems throughout the world, as no single
forest management standard is universally accepted, each taking a somewhat
different approach in defining standards for sustainable forest management.
Just as to provide some examples, we hereby list some common certification
standards:
> Forest Stewardship Council (FSC)39
> Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI)40
> Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification schemes (PEFC)41
Some criteria for the
award of the certificate to biofuel linked operations might regard, for instance,
the necessity to re-forest areas whose trees have been cut down to provide
biofuel industry with fresh timber.
The area of forest certified worldwide is growing rapidly. As of May 2006, there
were over 270 mil ha of forest certified under the CSA, FSC, SFI and other main
standards, representing around 7% of global forest area:42
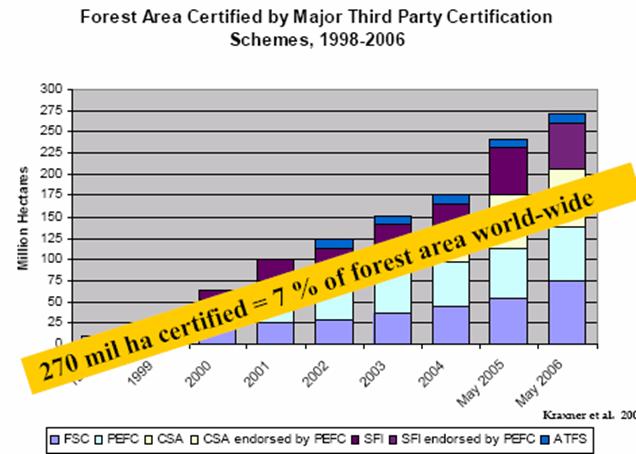
Unfortunately, to date most certified forestry operations are located in Europe
and North America but not in other vital areas for biofuels, such as Brazil.
Future policies and efforts should hence focus on these strategic regions, where
the development of such certifications is hindered by the lack of capacity to
undergo a certification audit and maintain operations to a certification
standard suffered by most organizations.
References
> Biofuels for transportation. Global potential and implications for sustainable
agriculture and energy in the 21st century
> International resource costs of biodiesel and bioethanol (UK Government,
Department for Transport)
> Parlak, Biofuels: Environmental and Economical Impact of Using Renewable
Energy Sources in Fossil Fuel Importing Countries
> EPA Tier I and Tier II health effects testing
> Life Cycle Inventory of Biodiesel and Petroleum Diesel for Use in an Urban
Bus, 1998, Sheehan, et. al.
> Farrell et al 2006. “Ethanol Can Contribute to Energy and Environmental Goals.”
Science 311: 506-508.
> National Biodiesel Board (NBB), Fact Sheets
> EPA "A Comprehensive Analysis of Biodiesel Impacts on Exhaust Emissions"
> World Resource Institute Policy note1, September 2006
> Brown, L. R., 1997, The Agricultural Link: How Environmental Deterioration
Could
> Disrupt Economic Progress:Worldwatch Institute,Washington, DC
> McNeely (IUCN):Biofuels: green energy or grim reaper? 2006
> George Monbiot, “Fuel for Naught,” The Guardian (London), November 23, 2004
> SRU, Reducing CO2 emisions from cars, 2005
> Vern Hofman, Biodiesel Fuel, AE-1240, North Dakota State University, February,
2003
> Gururaja, Biofuels and sustainable development: issue, challenges and options
(UNDESA/DSD)
> Pimentel and Tad W. Patzek; report available at Natural Resources Research (Vol.
14:1, 65-76)
> 12 Myths About Hunger based on World Hunger: 12 Myths, 2nd Edition, by Lappé,
et al, 1998
> Food for Thought by Elliott H. Gue - The Energy Letter February 22, 2006
> Potenziali areali italiani per colture dedicate da energia, P. Venturi, G.
Venturi, Rivista di ingegneria Agraria (2005)
> http://www.jatrophaworld.org/9.html
> www.heinzctr.org/ecosystems
> IEA: biofuels for transport, an international perspective, 2004
> http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethanol_fuel_in_Brazil
> EC Communication 8.2.2006, COM(2006) 34 Bruxelles
> Liquid biofuels for transportation in Tanzania, GTZ 2005
> World Energy Outlook 2006, IEA
> Potenziali areali italiani per colture dedicate da energia, P. Venturi, G.
Venturi, Rivista di ingegneria Agraria (2005)
> Von Braun, Pachauri, The promises and challenges of Biofuels for the poor in
developing countries. IFPRI 2006
> SAN: Sustainable Agriculture Standard, 2005
> Craxner: Forest Certification and certified forest products. 2006
> www.fsc.org
> http://www.aboutsfi.org/core.asp
> www.pefc.org
> http://www.transportenvironment.org/docs/presentations/2006/2006-06_biofuels/Lancaster_Presentation_pdf.pdf
(*) pietro.lanzini@yahoo.com.
1
Biofuels for transportation. Global potential and implications for sustainable
agriculture and energy in the 21st century.
2 International resource costs of biodiesel and bioethanol (UK
Government, Department for Transport).
3 Parlak, Biofuels: Environmental and Economical Impact of Using
Renewable Energy Sources in Fossil Fuel Importing Countries.
4 EPA Tier I and Tier II health effects testing.
5 Life Cycle Inventory of Biodiesel and Petroleum Diesel for Use
in an Urban Bus, 1998, Sheehan, et. al.
6 Farrell, Alexander E., Richard Plevin, Brian Turner, Andrew
Jones, Michael O’Hare, and Daniel Kammen. 2006. “Ethanol Can Contribute to
Energy and Environmental Goals.” Science 311: 506-508.
7 National Biodiesel Board (NBB), Fact Sheets.
8 EPA "A Comprehensive Analysis of Biodiesel Impacts on Exhaust
Emissions".
9 World Resource Institute Policy note1, September 2006.
10 Brown, L. R., 1997, The Agricultural Link: How Environmental
Deterioration Could Disrupt Economic Progress:Worldwatch Institute,Washington,
DC.
11 McNeely (IUCN):Biofuels: green energy or grim reaper? 2006.
12 George Monbiot, “Fuel for Naught,” The Guardian (London),
November 23, 2004.
13 SRU, Reducing CO2 emisions from cars, 2005.
14 Vern Hofman, Biodiesel Fuel, AE-1240, North Dakota State
University, February, 2003.
15 Gururaja, Biofuels and sustainable development: issue,
challenges and options (UNDESA/DSD).
16 Pimentel, Ethanol Fuels: Energy Balance, Economics, and
Environmental Impacts are Negative. Natural Resources Research, Vol. 12, No. 2,
June 2003.
17 Pimentel and Tad W. Patzek; report available at Natural
Resources Research (Vol. 14:1, 65-76).
18 12 Myths About Hunger based on World Hunger: 12 Myths, 2nd
Edition, by Lappé, et al, 1998.
19 Food for Thought by Elliott H. Gue - The Energy Letter
February 22, 2006.
20 Potenziali areali italiani per colture dedicate da energia,
P. Venturi, G. Venturi, Rivista di ingegneria Agraria (2005).
21 http://www.jatrophaworld.org/9.html.
22
http://64.233.161.104/search?q=cache:F0C6VA4C9bAJ:www.indiamart.com/aryanmushroom/+%22ad
vantages+of+Jatropha%22+biofuel&hl=it&gl=it&ct=clnk&cd=8 and
www.dayafterindia.com.
23
http://64.233.161.104/search?q=cache:D5QbRT4p2hsJ:www.socialtext.net/brightgreen/index.cgi%3Fjatropha+Jatropha+disadvantages&hl=it&gl=it&ct=clnk&cd=4.
24 Trabi, G.M. Gübitz, W. Steiner, N. Foidl: Toxicity of
Jatropha curcas seeds. Developed from the Symposium "Jatropha 97" Managua,
Nicaragua February 23 – 27, 1997.
25 Visit www.heinzctr.org/ecosystems.
26 Data taken from the IEA: biofuels for transport, an
international perspective, 2004.
27 Von Braun, Pachauri, The promises and challenges of Biofuels
for the poor in developing countries. IFPRI 2006.
28 Biofuels: Green energy or grim reaper? Jeff McNeely.
29 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethanol_fuel_in_Brazil.
30 Coelho: Brazilian sugarcane ethanol: lessons learned. 2005.
31 Economist.com “A ransom worth paying”, November 27th 2006.
32 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethanol_fuel_in_Brazil.
33 World Energy Outlook 2006, IEA.
34 Gururaja, Biofuels and sustainable development: issue,
challenges and options (UNDESA/DSD).
35 EC Communication 8.2.2006, COM(2006) 34 Bruxelles.
36 Liquid biofuels for transportation in Tanzania, GTZ 2005.
37 http://www.transportenvironment.org/docs/presentations/2006/2006-06_biofuels/Lancaster_Presentation_pdf.pdf.
38 SAN: Sustainable Agriculture Standard, 2005.
39 www.fsc.org.
40 http://www.aboutsfi.org/core.asp.
41 www.pefc.org.
42 Craxner: Forest Certification and certified forest products.
2006.
Pubblicato su
www.ambientediritto.it il 09/03/2007